Anyone who invests in a photovoltaic system or supplies their own household with solar power benefits all the more the more power the photovoltaic system produces. But how is solar power actually created? And does a photovoltaic system for self-consumption differ from a PV system that feeds electricity into the public grid? This article explains simply and briefly how a solar system works and how solar power is produced with a photovoltaic system.
How does a solar system work?

Electricity production with photovoltaics
Solar cells made of silicon
In principle, a solar system always works in the same way, regardless of whether it is a photovoltaic system on the roof or an open-space photovoltaic system. It also makes no difference whether the photovoltaic system is primarily used for self-consumption or whether the PV energy produced is fed into the public grid. The most important part of a PV system are the solar modules, which in turn consist of solar cells. These are made from silicon. Silicon is part of quartz sand. This occurs very frequently in nature, which makes silicon particularly cheap. Solar cells consist of several layers. Each layer is made of silicon. The top silicon layer is enriched with phosphorus atoms, the lower with boron atoms. This enables the electrons that are released when light hits the solar cells to be properly directed.
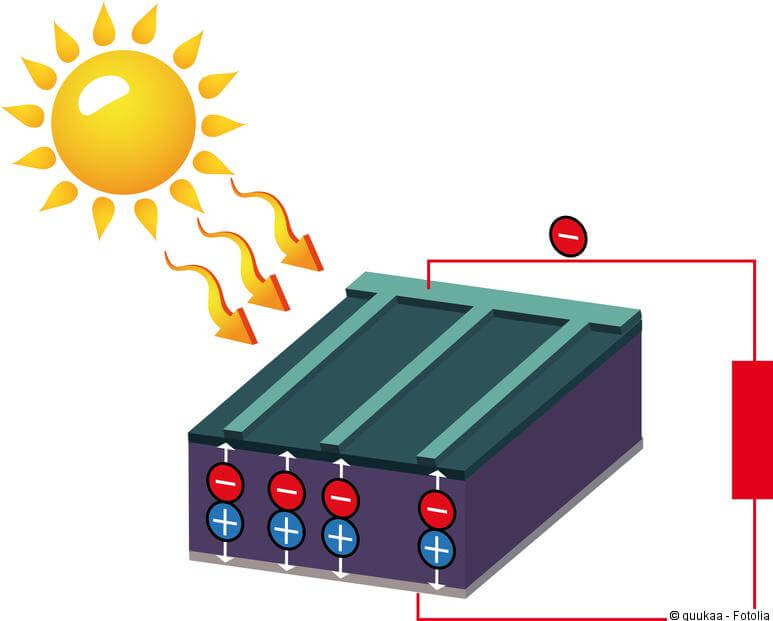
Source: solaranlagen.eu
Light falls on the photovoltaic modules
If sunlight falls on the photovoltaic modules, an electrical voltage is created. While negatively charged electrons collect on one side of the solar cells, positive charge carriers collect on the other. So there is a plus and minus pole like a battery. So that electricity can now flow, all that is needed is plates made of silver or aluminum that are wired together at the top and bottom of the solar cells. For use as solar modules, the solar cells are now packaged in a weatherproof manner with a pane of glass at the top and a protective film at the bottom. When installing the photovoltaic system, the solar modules are usually connected in series.
Electricity is not always electricity
The electricity produced by a photovoltaic system cannot, however, be used immediately for self-consumption or fed into the grid, as this is direct current. A PV inverter is required that converts the PV energy into household alternating current. The PV inverter is therefore an integral part of every photovoltaic system. It is located near the solar modules and is connected to the solar cells via cables.
When can solar power be produced?
A photovoltaic system works in principle as soon as the sun shines. In order to produce solar power, however, the weather does not have to be consistently excellent. Today’s PV modules can generate electricity with little light as well as with indirect light. Even when the sky is cloudy, solar power can be generated and converted via the inverter for self-consumption or for feeding into the grid.
Conclusion
A photovoltaic system converts light into electrical energy. This is done via the solar modules, which consist of solar cells with silicon. In order to be able to use the produced PV energy, it must be converted into alternating current via the PV inverter. What sounds relatively complicated is a simple physical process. The photovoltaic system offers a great advantage: PV modules are not only cheap, they are also extremely durable. Even 20 years after its installation, a solar system still produces as much solar power as it did at the beginning. There are hardly any performance losses measurable.